Google introduced Bard, an artificial intelligence chatbot, on February 6 in a blog post.
It was to be anticipated that Google would put a lot of effort into developing a reaction to ChatGPT’s rise to prominence, and Bard appears to be the search engine’s first attempt at competing with OpenAI’s chatbot.
We still don’t know a great deal about Google’s newly developed AI-powered tool.
In fact, access to it is currently restricted to only “trusted testers,” but hopefully, we hope it will soon be made available to the general public.
However, there is sufficient information available for us to provide information to you about some of the most pressing concerns regarding Bard AI.
What is Google Bard?
 Google Bard AI is an artificial intelligence chatbot that is similar to ChatGPT.
Google Bard AI is an artificial intelligence chatbot that is similar to ChatGPT.
Like ChatGPT, Google Bard is driven by a language model to have conversations with people.
The Language Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMDA) serves as the basis for Bard’s model, however, the company plans to begin with a scaled-down version of the comprehensive language model for the testing phase of the project.
How does Google Bard AI work?
Bard is an artificial intelligence created to carry on conversations, much like other chatbots.
This means that users engage with it by typing a question or request into a text box, and then the artificial intelligence, which in this case is Google Bard, will provide a response using a conversational tone.
The search for information is going to be the most obvious use case for Bard, but Google has suggested a few other use cases as well, such as arranging events, getting suggestions for lunch, and comparing films that were nominated for an Oscar.
In any case, it is reasonable to consider Bard as an approach to enhancing and broadening the capabilities of the search tools already offered by Google.
Features of Google’s Chatbot Bard
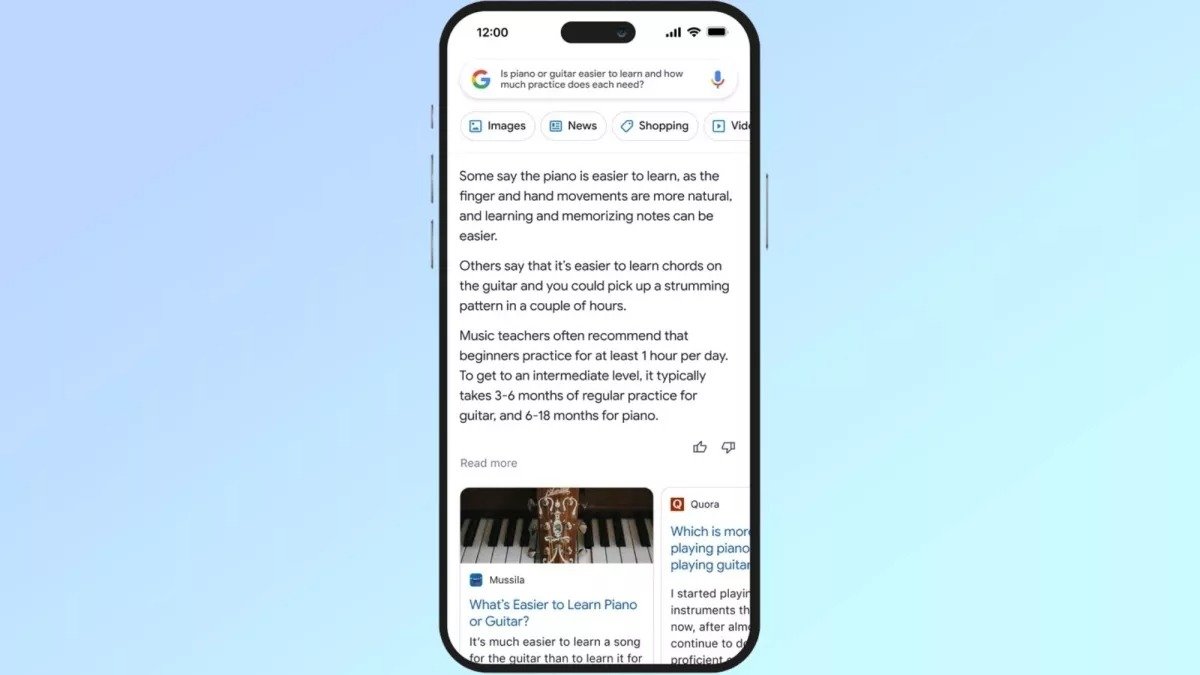 The focus of Google’s new AI will be on gathering feedback via Bard in order to improve the AI system in the future.
The focus of Google’s new AI will be on gathering feedback via Bard in order to improve the AI system in the future.
- Users will be able to see the combination of power, intelligence, and creativity in Google’s Chatbot Bard.
- Bard AI will continuously gather information from users via response and the web.
- The current version of BARD is actually Google’s lite model version of the LaMDA.
How can BARD be used?
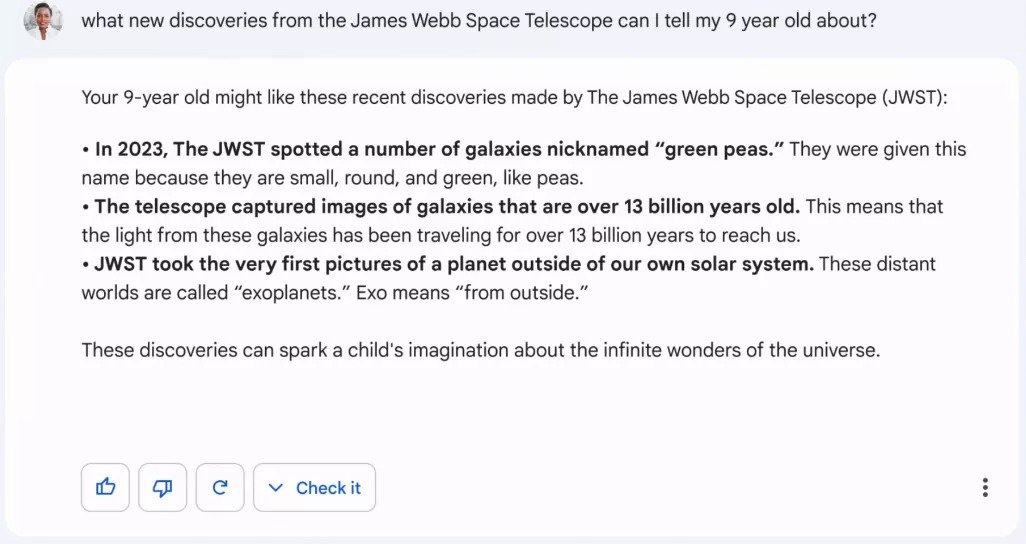 We do not have a complete understanding of all of Bard’s capabilities. However, Google has shown us a few examples, which are as follows:
We do not have a complete understanding of all of Bard’s capabilities. However, Google has shown us a few examples, which are as follows:
- Organize a baby shower for a close friend.
- Examining two films that were nominated for Oscars.
- Find inspiration for lunch based on what you already have in the refrigerator.
Who can use Google BARD AI?
At this time, the use of Bard AI is restricted to just “trusted testers.”
When ChatGPT was unveiled, it was available for public testing, and anyone interested could simply log in to OpenAI’s website and access the tool.
That, however, is not the case with Google’s new Bard. Since the AI is still in the testing phase, Google is not making it available to the general public, and only a few select users have access to it.
In addition, there is some good news. Since Google has stated that AI-powered features will be added to Google Search in the near future, let’s hope we won’t have to wait too long to evaluate Google Bard’s abilities.
Is Google BARD AI free to use?
Although Google has not yet provided confirmation one way or the other, it seems as though Bard will be free for the time being.
It would be surprising for Google to charge for the consumer usage of Bard (i.e. a version meant for everyday users) considering that it does not charge for Google Search; however, given that OpenAI-backed Microsoft already offers ChatGPT Plus as a subscription service, there’s an absolute possibility.
GOOGLE BARD VS CHATGPT: How can It Rival ChatGPT
 There are a number of subtle differences in the workings of the two models; however, the most significant difference is that training on the GPT-3.5 model was discontinued in 2021; as a result, some of the information it contains is now out of date.
There are a number of subtle differences in the workings of the two models; however, the most significant difference is that training on the GPT-3.5 model was discontinued in 2021; as a result, some of the information it contains is now out of date.
GPT-4 is expected to be released soon with up-to-date training. In the meantime, LaMDA is continuously being trained, which means that the information it produces may be more accurate and up-to-date than what ChatGPT generates.
As previously stated, Google Bard is already available to a small group of trusted testers. And Google says it will be available to the general public “in the coming weeks”.
Google also announced that the Generative Language API will be available for testing by individual developers, creators, and enterprises beginning next month.
LaMDA will initially power these APIs and will be expanded to include additional models.
Google Cloud also provides access to computing resources for startups developing AI systems through partnerships with Cohere, C3.ai, and Anthropic.
In conclusion
Minutes after Google announced Bard, Microsoft revealed that it will conduct its own live event, the day before, at its headquarters in Redmond, Washington. This means there is some sort of rivalry between these companies in the aspect of integrating AI into their search engines.
Microsoft didn’t reveal that it would announce the addition of ChatGPT to Bing at the event, but it’s widely believed that this is the case given the company’s recent $10 billion investment into OpenAI and reports of the existence of an AI-assisted version of Bing.
Not much is known about Microsoft’s or Google’s plans to address the issue of a conversational AI returning misleading results in response to user inquiries, but if they succeed, it might revolutionize the way we conduct web searches.