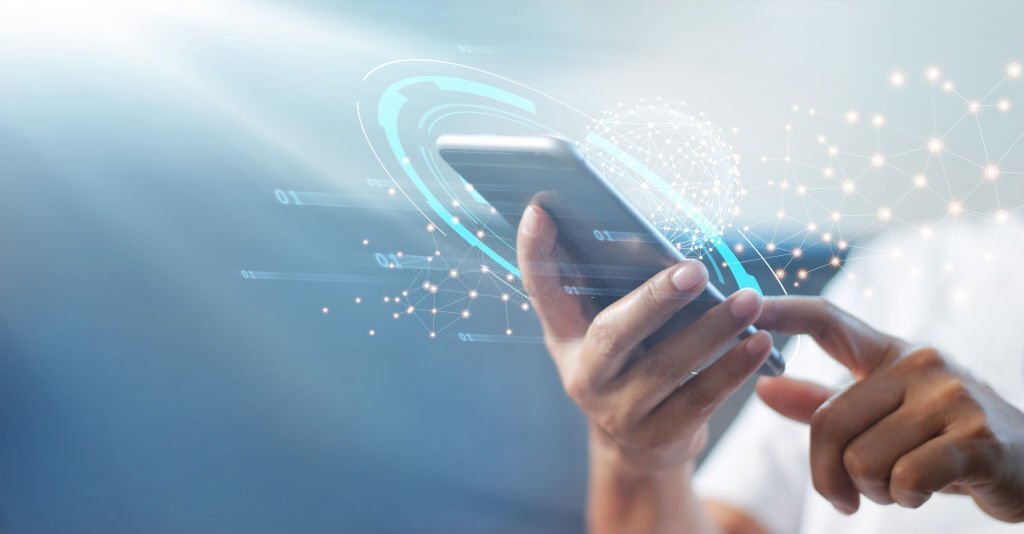
Mobile data has become an integral part of modern life, enabling users to stay connected and access a wide range of services and applications.
Ever found yourself wondering: What is mobile data? Definition, types and examples, you ask? Well, you’re in luck!
In this article, we’ll delve into the nitty-gritty of mobile data, breaking down the complex terms into simple, digestible information. So sit back, relax, and let’s get cracking!
What is Mobile Data?
Mobile data, in a nutshell, is the ability to access the internet on your mobile device using a cellular network, without relying on Wi-Fi.
Imagine you’re out and about, with no Wi-Fi hotspot in sight, but you need to check your email, browse social media, or stream your favorite tunes. That’s where mobile data swoops in to save the day!
By connecting to your mobile service provider’s network, you can surf the web, chat with friends, and even use GPS to navigate unfamiliar terrain – all without being tethered to a Wi-Fi network.
Key Takeaways
- Mobile data allows internet access on devices through cellular networks without Wi-Fi.
- Different generations of mobile data include 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G, each offering improved speed and performance.
- Mobile data usage depends on individual habits, such as web browsing, streaming, and app usage.
- To monitor mobile data usage, use built-in tracking on your device or your service provider’s app or website.
- With 4G, streaming videos and downloading large files became a breeze, revolutionizing the way we use our mobile devices.
- 5G is the latest generation of mobile data technology, designed to deliver ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and increased network capacity.
Types of Mobile Data
Now that we’ve established what mobile data is, let’s explore the various types and how they differ from one another.
1. First generation or 1G
1G sent voice over cellular networks by utilizing analog telecommunications technologies, which were first made available in 1979 and continued to be used throughout the 1980s. 1G networks did not transfer mobile data. It’s kind of odd adding it here but I felt like. #lol
2. 2G (Second Generation)
2G was the first mobile data technology that allowed digital voice calls and text messaging. It introduced the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) and provided data transfer rates of up to 64 kbps (kilobits per second). Examples of 2G technologies include GSM, CDMA, and GPRS.
3. 3G (third Generation)
3G, or third-generation, mobile data technology was a game-changer when it first hit the scene. It made surfing the web on your mobile device a more enjoyable experience, with faster download and upload speeds compared to its predecessors.
However, as with all things tech-related, 3G eventually gave way to more advanced technologies – but it’s still hanging in there, providing a dependable connection in areas with limited coverage.
3G networks offer data transfer rates of up to 2 Mbps (megabits per second). Examples of 3G technologies include UMTS, CDMA2000, and HSPA.
4. 4G (Fourth Generation)
Enter 4G, the fourth-generation mobile data technology, which blew 3G out of the water with its lightning-fast speeds.
4G networks provide even faster data transfer speeds and improved network capacity, enabling high-definition video streaming, online gaming, and seamless video conferencing.
4G networks can achieve data transfer rates of up to 100 Mbps for mobile devices and 1 Gbps for stationary devices. Examples of 4G technologies include LTE (Long-Term Evolution) and WiMAX.
But the quest for speed didn’t end there…
5. 4G LTE: Kicking It up a Notch
4G LTE (Long-Term Evolution) took the already impressive 4G technology and supercharged it. Offering even faster data speeds and improved network capacity, 4G LTE allowed for seamless streaming, video calling, and online gaming on the go.
And yet, the innovation train kept chugging along…
6. 5G (Fifth Generation)
The latest and greatest in mobile data technology, 5G (fifth-generation), has taken the world by storm. With mind-blowing speeds and reduced latency, 5G is set to revolutionize not just mobile data, but also the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and more.
5G networks can potentially achieve data transfer rates of up to 20 Gbps and have the ability to support a vast number of connected devices, paving the way for new applications and services.
Examples of 5G technologies include New Radio (NR) and millimeter-wave (mmWave) bands.
Mobile data is a service provided by cellular network providers that allows users to access the internet on their mobile devices without the need for a Wi-Fi connection. It utilizes a range of cellular frequencies and technologies, such as 3G, 4G, and 5G, to provide internet connectivity.
Overview of Mobile Data Generations and Their Key Features
| Generation | Type of Mobile Data | Year of Introduction | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1G | Analog Cellular | 1980s | Voice-only communication, limited capacity, poor security |
| 2G | Digital Cellular | Early 1990s | Text messaging (SMS), improved call quality, better security |
| 2.5G | GPRS | Late 1990s | First introduction of mobile data, low-speed data transmission |
| 2.75G | EDGE | 2000s | Enhanced data rates, faster than GPRS |
| 3G | UMTS | Early 2000s | High-speed data, video calling, mobile broadband |
| 3.5G | HSPA | Mid-2000s | Faster data rates, improved network capacity |
| 4G | LTE | 2009 | High-speed mobile broadband, improved capacity, lower latency |
| 4.5G | LTE Advanced | Early 2010s | Faster data rates, increased capacity, carrier aggregation |
| 5G | 5G NR | 2019 | Ultra-high-speed data, low latency, massive device connectivity |
Examples of Mobile Data Usage
Curious about how mobile data impacts our everyday lives? Here are a few examples that showcase the power of mobile data:
1. Web Browsing
Mobile data enables users to access websites and online content on their mobile devices, making it easy to search for information, read news articles, or check social media while on the go.
2. Video and Music Streaming
Users can stream video content from platforms like YouTube and Netflix or listen to music on services like Spotify and Apple Music using mobile data.
3. Instant Messaging and Video Calling
Mobile data allows users to send and receive instant messages, images, and videos through apps like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and Snapchat. It also supports video calling through apps like Skype, Zoom, and Google Meet.
4. Online Gaming
Mobile data enables users to play online games on their mobile devices, either through dedicated gaming apps or by accessing browser-based games.
5. Navigation and Location Services
Gone are the days of getting lost and frantically searching for a physical map. With mobile data, GPS navigation apps like Google Maps and Waze help us find our way, providing real-time traffic updates and alternate routes.
Using mobile data, users can access GPS-based navigation and location services helping them find directions, locate nearby points of interest, and receive real-time traffic updates.
6. Mobile Banking
Need to transfer money, pay bills, or check your account balance? Mobile data makes it possible to manage your finances securely and conveniently through banking apps, without having to visit a physical branch.
7. E-Commerce
Shopping for clothes, gadgets, or even groceries has never been easier. Thanks to mobile data, you can browse and purchase items from the comfort of your smartphone, with just a few taps on the screen.
Popular e-commerce platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Walmart can be accessed using mobile data.
8. Email Access
Mobile data allows users to access their email accounts, send and receive messages, and manage their inboxes on the go. Popular email clients like Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo Mail can be used on mobile devices with the help of mobile data.
9. Cloud Services
Using mobile data, users can access various cloud services to store, manage, and share files, photos, and documents. Cloud services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and iCloud enable users to sync data across multiple devices and access their files from anywhere.
10. Mobile Payments and Digital Wallets
Mobile data enables users to make mobile payments, transfer money, and manage their digital wallets through apps like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal.
These services allow users to make contactless payments and manage their finances on the go.
11. Social Media
Users can access social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn through mobile data, staying connected with friends, family, and professional contacts.
Mobile data enables users to share updates, photos, and videos, as well as engage with other users’ content.
Managing Mobile Data Usage
As mobile data usage continues to grow, it’s essential to monitor and manage your data consumption to avoid exceeding your monthly data allowance or incurring additional charges.
Here are some tips to help you manage your mobile data usage:
1. Track your data usage
Most smartphones and mobile devices have built-in data usage tracking features that can help you monitor your consumption and set limits or alerts.
2. Adjust app settings
Some apps consume more data than others. Adjust the settings of data-hungry apps to restrict background data usage or lower the quality of streaming content.
3. Use Wi-Fi whenever possible
Connect to Wi-Fi networks at home, work, or public places to save mobile data. Many businesses, restaurants, and public spaces offer free Wi-Fi access.
4. Offline mode
Some apps, like music and video streaming services, allow you to download content for offline use. Downloading content while connected to Wi-Fi can help save mobile data.
5. Choose the right data plan
Assess your mobile data needs and choose a plan that offers a suitable data allowance. Some mobile carriers also offer unlimited data plans or data rollover options.
FAQs on Mobile Data
As mobile data technology continues to advance, it will play an increasingly important role in shaping the way we live, work, and communicate.
By managing mobile data usage effectively and prioritizing security and privacy, users can make the most of this powerful tool while minimizing potential risks.
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to mobile data:
How do I start using mobile data?
To start using mobile data, you’ll need a mobile device with cellular capabilities, a SIM card, and a data plan from a cellular service provider. Insert the SIM card into your device, activate your data plan, and enable mobile data in your device’s settings.
What are 3G, 4G, and 5G?
3G, 4G, and 5G are generations of mobile data technology. Each generation offers faster internet speeds and improved performance compared to its predecessor. 3G stands for third generation, 4G for fourth generation, and 5G for fifth generation.
Do I need a separate plan for mobile data?
Most cellular service providers offer plans that include a combination of voice minutes, text messages, and mobile data. You can choose a plan that best suits your needs based on how much mobile data you expect to use.
How do I know if my device is using mobile data or Wi-Fi?
Most smartphones display a Wi-Fi or mobile data icon in the status bar at the top of the screen. When connected to Wi-Fi, you’ll see a Wi-Fi icon, and when using mobile data, you’ll see an icon that represents the type of mobile data connection (e.g., 3G, 4G, or 5G).
How can I monitor my mobile data usage?
You can monitor your mobile data usage through your device’s settings, usually under the “Mobile Data” or “Cellular Data” section. Additionally, your service provider may offer an app or website where you can track your data usage.
What is data throttling?
Data throttling is when your service provider intentionally reduces your mobile data speed after you’ve reached a certain usage limit. This is often done to manage network congestion or to enforce data limits on your plan.
What is mobile data roaming?
Mobile data roaming refers to using your mobile data while connected to a cellular network outside of your service provider’s coverage area. This often occurs when you travel internationally. Data roaming may result in additional charges, so it’s important to check with your service provider about their roaming policies before traveling.
How can I conserve mobile data?
To conserve mobile data, connect to Wi-Fi whenever available, limit video streaming and large file downloads, disable automatic app updates, and use data-saving modes in your apps and browser.
Is mobile data usage billed differently from voice calls and text messages?
Mobile data usage is typically billed separately from voice calls and text messages. Your cellular plan may include a set amount of data, with additional charges or speed reductions if you exceed the limit. Some providers offer unlimited data plans, but these may be subject to speed throttling or other restrictions.
What is the difference between mobile data and Wi-Fi?
The main difference between mobile data and Wi-Fi lies in their connection sources. Mobile data uses cellular networks provided by mobile service providers, while Wi-Fi connects to the internet through a local wireless network created by a Wi-Fi router or access point.
Does mobile data cost money?
Yes, using mobile data typically incurs charges from your mobile service provider. These charges can be based on a pay-as-you-go model or included in a monthly plan with a set data allowance.
How can I check how much mobile data I’ve used?
You can monitor your mobile data usage through your device’s settings or by using an app designed for this purpose. Additionally, many mobile service providers offer online account management tools that let you track your data usage.
Can I use mobile data while traveling abroad?
Yes, but be aware that using mobile data while roaming can lead to hefty charges. To avoid unexpected bills, check with your mobile service provider about their international roaming plans or consider purchasing a local SIM card at your destination.
How do I conserve mobile data usage?
Some tips to minimize mobile data usage include connecting to Wi-Fi whenever possible, limiting video streaming, using data-saving features in apps, and disabling background app refresh.
See also: All Technology Terms Explained
Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced, always-on world, mobile data has become an essential part of our daily lives. As we’ve explored, mobile data is the lifeblood that fuels our ability to stay connected, informed, and entertained, regardless of our location.
With advancements in technology, such as 5G, the potential applications and benefits of mobile data are bound to grow even further.
So, the next time you ask, “What is mobile data? Definition, types and examples,” you’ll have the answers at your fingertips. From humble beginnings with 3G to the incredible speeds of 5G, mobile data has transformed the way we communicate and interact with the world around us. And with the continuous evolution of this technology, who knows what exciting developments lie just around the corner?
Click the button below to Gain Access to our Members’ Exclusive Group, before it fills up again.
Gain Access Now!
See what others are reading: